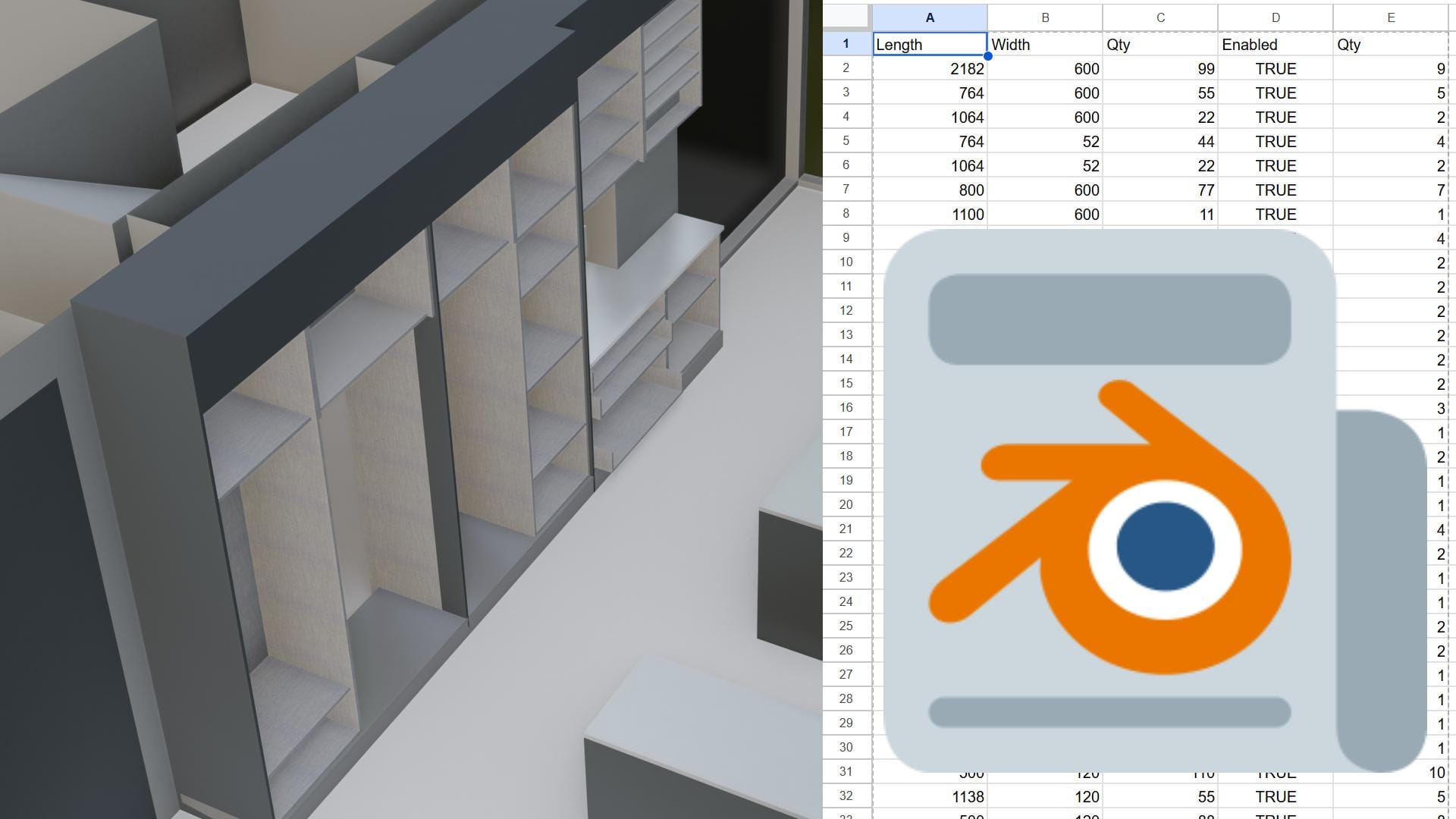
Using Blender for furniture is quite convenient. You can make changes to furniture very quickly for your customers. Blender can be used for both visualization and production. I will show you step by step how many panels your designed furniture will require.
In Europe, the Middle East, and the East, MDF or particleboard is mostly used. For custom production, the thickness is 18mm. America uses plywood more. We will go with MDF here.
In your project, you should design the objects to be 18mm thick. Otherwise, your cuts will be wrong as a result of an error.
First, you need to select the furniture. Use Ctrl+A to reset the scale and rotation. Open the scripting workspace. You need to paste the code I will give you here. You can change the name for the cutting list at the top of the code.
import bpy
import csv
import os
from mathutils import Vector
from collections import defaultdict
# --- Desktop Path ---
desktop_path = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), "Desktop")
csv_path = os.path.join(desktop_path, "kitchen.csv")
# === Helper Functions ===
def get_1d_overlap(min1, max1, min2, max2, tolerance_mm=1.0):
"""
Returns the overlap length of two 1D intervals (in meters).
tolerance_mm: if overlap is smaller than this mm, treat as 0 (filters line contact).
"""
# world dimensions are in meters, convert tolerance to meters
tol = tolerance_mm / 1000.0
overlap_len = max(0.0, min(max1, max2) - max(min1, min2))
return overlap_len if overlap_len > tol else 0.0
def get_sorted_dimensions_mm(obj):
"""Returns object dimensions SORTED (Short, Medium, Long) in mm."""
dims = [obj.dimensions.x, obj.dimensions.y, obj.dimensions.z]
dims_mm = [round(d * 1000, 2) for d in dims]
return tuple(sorted(dims_mm, reverse=True))
def get_raw_dimensions_mm(obj):
"""Returns object dimensions as raw (X, Y, Z) in mm."""
dims = [obj.dimensions.x, obj.dimensions.y, obj.dimensions.z]
dims_mm = [round(d * 1000, 2) for d in dims]
return dims_mm
def get_orientation(dims_xyz_mm):
"""Determines object orientation based on X, Y, Z dimensions."""
x, y, z = dims_xyz_mm
return "Vertical" if z >= x and z >= y else "Horizontal"
def face_world_bounds(obj):
"""Returns world coordinate min/max bounds of the object (in meters)."""
coords = [obj.matrix_world @ v.co for v in obj.data.vertices]
xs = [c.x for c in coords]
ys = [c.y for c in coords]
zs = [c.z for c in coords]
return min(xs), max(xs), min(ys), max(ys), min(zs), max(zs)
def get_band_sides(obj, others, all_bounds_cache, thickness_mm=18.0, tolerance_mm=0.5, area_tol_mm=1.0):
"""
Determines which edges of the object need banding.
- thickness_mm: panel thickness check (mm)
- tolerance_mm: edge alignment tolerance (mm)
- area_tol_mm: minimum overlap for surface contact (mm) => filters line contact
"""
# world dimensions in meters; convert tolerances to meters
tol = tolerance_mm / 1000.0
area_tol = area_tol_mm / 1000.0
dims_mm = get_raw_dimensions_mm(obj) # [X, Y, Z] mm
# 1. Determine thickness axis
thickness_axis = None
edge_axes = []
if abs(dims_mm[0] - thickness_mm) < tolerance_mm:
thickness_axis = "X"; edge_axes = [("Y", dims_mm[1]), ("Z", dims_mm[2])]
elif abs(dims_mm[1] - thickness_mm) < tolerance_mm:
thickness_axis = "Y"; edge_axes = [("X", dims_mm[0]), ("Z", dims_mm[2])]
elif abs(dims_mm[2] - thickness_mm) < tolerance_mm:
thickness_axis = "Z"; edge_axes = [("X", dims_mm[0]), ("Y", dims_mm[1])]
else:
return "" # not an 18mm panel
# Shelf rule
if "raf" in obj.name.lower() or "shelf" in obj.name.lower():
return "Long Long Short Short"
# Short and Long edge labeling
axis_1, dim_1 = edge_axes[0]
axis_2, dim_2 = edge_axes[1]
if abs(dim_1 - dim_2) < 0.5:
long_axis, short_axis = axis_1, axis_2
elif dim_1 > dim_2:
long_axis, short_axis = axis_1, axis_2
else:
long_axis, short_axis = axis_2, axis_1
sides_to_check = {
f"{long_axis}-": "Short", f"{long_axis}+": "Short",
f"{short_axis}-": "Long", f"{short_axis}+": "Long"
}
# Self bounds (meters)
self_bounds = all_bounds_cache[obj.name]
all_bounds_coords = {
"X-": self_bounds[0], "X+": self_bounds[1],
"Y-": self_bounds[2], "Y+": self_bounds[3],
"Z-": self_bounds[4], "Z+": self_bounds[5]
}
band_labels = []
for side_name, label in sides_to_check.items():
axis_name = side_name[0] # 'X' or 'Y' (not Z)
value = all_bounds_coords[side_name] # world coordinate (meters)
touching = False
for other in others:
if other == obj or other.type != 'MESH':
continue
other_bounds = all_bounds_cache[other.name]
other_coords = {
"X-": other_bounds[0], "X+": other_bounds[1],
"Y-": other_bounds[2], "Y+": other_bounds[3],
"Z-": other_bounds[4], "Z+": other_bounds[5]
}
# Opposite side coordinate: if our side is '-', other's '+' should match
other_val = other_coords[f"{axis_name}+"] if "-" in side_name else other_coords[f"{axis_name}-"]
# If surfaces are aligned (touching condition)
if abs(value - other_val) <= tol:
# calculate AREA overlap in the other two axes
overlap_axes = [ax for ax in ["X", "Y", "Z"] if ax != axis_name]
ax1, ax2 = overlap_axes[0], overlap_axes[1]
# self ranges (meters)
self_min_ax1 = all_bounds_coords[f"{ax1}-"]
self_max_ax1 = all_bounds_coords[f"{ax1}+"]
self_min_ax2 = all_bounds_coords[f"{ax2}-"]
self_max_ax2 = all_bounds_coords[f"{ax2}+"]
other_min_ax1 = other_coords[f"{ax1}-"]
other_max_ax1 = other_coords[f"{ax1}+"]
other_min_ax2 = other_coords[f"{ax2}-"]
other_max_ax2 = other_coords[f"{ax2}+"]
# overlap lengths (meters)
overlap_1 = get_1d_overlap(self_min_ax1, self_max_ax1, other_min_ax1, other_max_ax1, tolerance_mm=area_tol_mm)
overlap_2 = get_1d_overlap(self_min_ax2, self_max_ax2, other_min_ax2, other_max_ax2, tolerance_mm=area_tol_mm)
# If there's at least area_tol in both axes, there's AREA contact
if overlap_1 > 0.0 and overlap_2 > 0.0:
touching = True
break # no need to check further for this surface
if not touching:
band_labels.append(label)
band_labels.sort(reverse=True)
return " ".join(band_labels)
# === Main Process ===
objs = [o for o in bpy.context.selected_objects if o.type == 'MESH']
groups = defaultdict(list)
print(f"Processing {len(objs)} mesh objects...")
# --- BOUNDS cache (in meters) ---
all_bounds_cache = {obj.name: face_world_bounds(obj) for obj in objs}
def bbox_data(obj):
"""Returns world-space bounding box min-max coordinates of the object."""
box = [obj.matrix_world @ Vector(corner) for corner in obj.bound_box]
min_v = Vector((min(v.x for v in box), min(v.y for v in box), min(v.z for v in box)))
max_v = Vector((max(v.x for v in box), max(v.y for v in box), max(v.z for v in box)))
return min_v, max_v
def bbox_intersects_deep(obj1, obj2, min_overlap=0.001):
"""Checks if objects overlap by at least min_overlap (in meters)."""
min1, max1 = bbox_data(obj1)
min2, max2 = bbox_data(obj2)
overlap_x = min(max1.x, max2.x) - max(min1.x, min2.x)
overlap_y = min(max1.y, max2.y) - max(min1.y, min2.y)
overlap_z = min(max1.z, max2.z) - max(min1.z, min2.z)
if overlap_x > min_overlap and overlap_y > min_overlap and overlap_z > min_overlap:
return True
return False
def has_inner_channel(obj, all_objs):
"""Checks if there's another object approximately 8mm thick inside this object (excluding touching)."""
for other in all_objs:
if other == obj or other.type != 'MESH':
continue
# Find objects with thickness around 8mm
dims = [d * 1000 for d in other.dimensions]
if not any(7.5 <= d <= 8.5 for d in dims):
continue
# Check if truly overlapping (not just touching)
if bbox_intersects_deep(obj, other, min_overlap=0.001): # must overlap by 1mm
return True
return False
# Group objects
groups = defaultdict(list)
all_objs = [o for o in bpy.context.selected_objects if o.type == 'MESH']
for obj in objs:
dims_sorted = get_sorted_dimensions_mm(obj)
dims_xyz_mm = get_raw_dimensions_mm(obj)
orientation = get_orientation(dims_xyz_mm)
face_count = len(obj.data.polygons)
channel = "✔" if has_inner_channel(obj, all_objs) else ""
cnc = "✔" if face_count > 10 else ""
# You can adjust these parameters:
# thickness_mm = 18.0, tolerance_mm = 0.5 (edge alignment), area_tol_mm = 1.0 (min overlap area)
band_sides = get_band_sides(obj, objs, all_bounds_cache, thickness_mm=18.0, tolerance_mm=0.5, area_tol_mm=1.0)
key = (dims_sorted, orientation, channel, cnc, band_sides)
groups[key].append(obj.name)
# === Write to CSV in the specified format ===
with open(csv_path, mode='w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(['Length', 'Width', 'Qty', 'Enabled'])
for (dims_sorted, orientation, channel, cnc, band_sides), names in groups.items():
# dims_sorted is (longest, middle, shortest)
# For the output format: Length = longest, Width = middle
length = dims_sorted[0] # longest dimension
width = dims_sorted[1] # middle dimension
qty = len(names)
enabled = "TRUE"
writer.writerow([length, width, qty, enabled])
print(f"✅ CSV file successfully saved: {csv_path}")
After running this code, it will give you a csv code.
Go to cutlistoptimizer. Click on the CSV import option. You can enter the plate size you are using or the extra plate sizes you have available below. The plate size we are using is 2800 x 2100 mm. You can enter the extra number here; the reason for this is so that the project does not end if the number of plates is insufficient. Then press the calculate button.
As you can see, 18 plates were used, which is 81% of the total. We have 19% waste. You can use this waste in your future projects.
If you use Blender for furniture or architecture, please like the video and mention it in the description. Stay tuned for more videos.